© Borgis - New Medicine 1/2006, s. 15-18
Danuta Rosołowska-Huszcz, Katarzyna Lachowicz
Influence of dietary fat on thyroid hormone plasma concentrations
Department of Dietetics, Warsaw Agricultural University, Warsaw, Poland
Head of Department: professor dr hab. Joanna Gromadzka-Ostrowska MD, PhD
Summary
SUMMARY
INTRODUCTION: Both fatty acids and thyroid hormones regulate energy metabolism influencing energy production and dissipation. Effect of thyroid hormones on fatty acid metabolism is well known. Reciprocal action fatty acids on thyroid activity is not yet fully characterized. The aim of study was to compare the effect of dietary fish oil and lard on thyroid hormone plasma concentration.
Material and method: Male Wistar rats (n=36) five weeks old were divided into six groups receiving during six weeks different levels (w/w 5% – LF diet, 10% – MF, 20% – HF) and kinds of dietary fat (fish oil – group F and lard – group L).
Results: Total thyroxine level was higher in group L than F irrespective of dietary fat level, free thyroxine did not differ in groups F and L on LF and HF diets and it was higher in group L on MF diet. Triiodothyronine level was higher in group L on LF and MF diets, whereas reverse triiodothyronine – on LF and HF diets. Total thyroxine, triiodothyronine and revers triiodothyronine levels did not respond to dietary fat level.
Conclusions: The effect of dietary fat composition on thyroid hormone plasma level could depend on amount of fat intake. Lard intake induces higher plasma levels of thyroid hormones than fish oil. Higher thyroid hormones level, revers triiodothyronine including, suggests decrease in liver deiodinating activity in rats receiving lard.
Introduction
Fatty acids influence energy metabolism both as substrates for oxidative pathways [1] and regulators of expression of proteins controlling fatty acid metabolism – fatty acid synthesis [2, 3] and oxidation [4], lipolysis [3, 4] and energy dissipation [4, 5]. The same reactions are controlled by thyroid hormones [6-8]. Fatty acids have been shown to influence thyroid hormone plasma level. Elevation of free fatty acid plasma concentration induced by heparin treatment or pathological conditions have been found to increase free thyroxine (T4) plasma concentration by competition with T4 binding with plasma proteins [9-12]. This leads to increase in inhibition of thyrotropin secretion and decline in thyroid activity [11, 13]. Effect of dietary fat composition on thyroid hormone plasma concentrations was reported as well [5, 13, 14-18]. However, the results from in vivo and in vitro studies displayed discrepancies which could arise from the possible multifacial impact of fatty acids on thyroid axis activity. To extend knowledge about influence of dietary fat on thyroid activity we compared plasma levels of T4 both total and free (fT4), triiodothyronine (T3), reverse T3 (rT3) in rats fed fish oil – rich in polyunsaturated n-3 fatty acids and lard treated as source of saturated and monounsaturated fatty acids.
Material and method
Male Wistar rats (from Medical Research Center of Polish Academy of Sciences, Warsaw, Poland) were roared from five weeks of life in standard environmental conditions (L/D 12/12, 23°C, 50-65% humidity) with food and water supplied ad libitum. The animals were divided in dietary groups (n=6) differing in kind (fish oil – groups F and lard – groups L) and amount of dietary fat (w/w 5% – LF diet, 10% – MF diet and 20% – HF diet). After six weeks of animal breeding the rats were anesthetized by ether and blood was taken by cardiac puncture. Plasma was stored at -20°C till the hormone assays.
Thyroxine both total and free, T3 and rT3 plasma concentrations were determined by radioimmunoassay commercial kits. For T4 (sensitivity 12.8 nmol/L, intraassay variation 5.3%, interassay variation 4.1%) and T3 (sensitivity 0.154 nmol/l, intraassay variation 3.8, interassay variation 5.4%) kits were produced by POLATOM, for fT4 (sensitivity 0.8 pmol/L, intraassay variation 5%, interassay variation 7%) by Orion Diagnostica, for rT3 (sensitivity 0.014 nmol/L, intraassay variation 6.5%, interassay 7.6%) by Biochem Immunosystems.
Results
Body weight gain and food intake
Initial body weight did not differ between dietary groups. Dietary fat level and composition did not influence body weight gain.
Daily food intake expressed in g of diet relatively to final body weight decreased as dietary fat level rose (p<0.001), whereas it did not depend on fat composition. Total energy intake was higher in group L in rats fed LF and HF diets (p<0.03 and p<0.01 – respectively). Dietary fat level affected energy intake in group L. It was higher in rats on HF than LF and MF diets (p<0.03 and p<0.05 – respectively) – Table 1.
Table 1. Initial body weight, daily body weight gain and intakes of food and total energy in rats fed experimental diets.*
| Variables | Diets | Dietary groups |
| F | L |
| Mean | SE | Mean | SE |
| Initial body weight (g) | LF | 277.8 | 3.35 | 277.3 | 2.48 |
| MF | 274.3 | 4.22 | 271.3 | 8.64 |
| HF | 276.5 | 4.85 | 267.7 | 10.84 |
| Daily body weight gain (g) | LF | 3.27 | 0.18 | 3.46 | 0.17 |
| MF | 3.53 | 0.19 | 2.99 | 0.19 |
| HF | 3.71 | 0.19 | 3.59 | 0.35 |
| Food intake (g /day/100g of final body weight) | LF | 5.22C | 0.08 | 5.16B | 0.05 |
| MF | 4.79B | 0.04 | 4.93A | 0.03 |
| HF | 4.34A | 0.16 | 4.74A | 0.07 |
| Total energy intake (kJ /day/100g final body weight) | LF | 74.63a | 1.16 | 79.40Ab | 2.05 |
| MF | 76.12 | 1.72 | 79.88A | 1.17 |
| HF | 78.50a | 2.94 | 84.15Bb | 1.21 |
Hormone concentrations in plasma
Dietary fat composition significantly affected T3 concentration in rats fed LF and MF diets. Lower values was observed in group F than L (p<0.0035 on LF diet and p<0.007 on MF). In rats receiving HF diet T3 level was not affected by kind of dietary fat (Figure 1 – panel A). Total thyroxine plasma concentration was lower in group F in rats fed all fat amounts (p<0.000001 on LF, p<0.000001 on MF, p<0.0005 on HF diets; Figure 1 – panel B). Dietary fat level did not inluence T3 and T4 concentration both in fish oil and lard given rats.
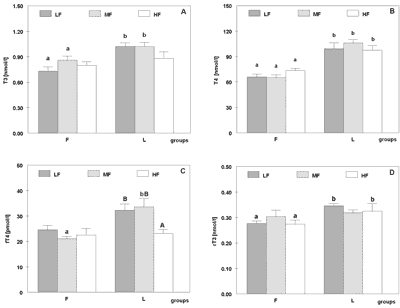
Fig. 1. Plasma triiodothyronine (T3 [nmol/l] – panel A), total thyroxine (T4 [nmol/l] – panel B), free thyroxine (fT4 [pmol/l] – panel C) and revers triiodothyronine (rT3 [nmol/l] – panel D) concentrations in rats fed diets containing 5% (LF), 10% (MF) or 20% (HF) (w/w) of fish oil (group F) or lard (group L) during six weeks of experiment.
Values are expressed as mean with their standard errors for six animals.
different a, b letters indicate significant differences between groups F and L (p<0.05)
different A, B letters indicate significant differences within groups F and L (p<0.05).
Free T4 concentration was affected by dietary fat composition in rats fed MF diet only. It was lower in group F (p<0.005). The level of dietary fat influenced fT4 concentration in group L – it was lower in rats fed HF diet than in rats which were given LF (p<0.04) and MF (p<0.02) diets (Figure 1 – panel C).
Free T4 index did not depend on dietary fat level and composition.
Reverse T3 concentration was influenced by dietary fat composition in rats fed LF and HF diets, where it was significantly higher in group L (p<0.00007 on LF and p<0.0002 on HF diets), whereas it did not respond to dietary fat level (Figure 1 – panel D).
Discussion
The concentrations of thyroid hormones in blood plasma - T4, fT4, T3 and rT3 were found in our experiment to be affected by dietary fat composition. They were lower in rats fed diet with n-3 PUFA rich fish oil than in rats given diets with lard. This is rather surprising taking into consideration the results reported by others showing lower plasma level of T4 and T3 in rats fed saturated, animal fats than polyunsaturated, plant oil receiving [16]. Lack of differences in T3 concentrations in rats fed prime rib, tallow or stearate diets and in T3 and T4 concentrations in pigs fed rapeseed or sunflower seed meals was also observed [15, 19]. However, lower T4 level was observed in rats fed fish than safflower oil given [5]. Our results indicate that the effect of dietary fat composition should be analysed jointly with the influence of fat level since T3 and fT4 concentrations were not influenced by kind of fat in rats on HF diet and fT4 level additionally in rats obtaining LF diet. The effect of our dietary manipulations on T4 and fT4 level is difficult to explain. Total T4 concentration was higher in group L in all animals whereas effect of fat composition on fT4 level seems to be bimodal since it was not seen on LF and HF diets. It is noteworthy that fT4 index was affected neither fat level nor its composition.
Reverse T3 plasma concentration reflects hepatic deiodinase type I (DI) activity in opposed manner, it rises with decline in DI activity. Thus, higher rT3 concentration seen in group L could indicate lower DI activity. This could be explained by lower expression of T3 receptor observed on diet rich in saturated fatty acids [20] since T3 acting through its receptor has been shown to stimulate DI gene transcription [21].
Conclusions
1. The effect of dietary fat composition on thyroid hormone plasma level could depend on amount of fat intake.
2. Lard intake induces higher plasma levels of T4, fT4, T3 and rT3 than fish oil.
3. Higher thyroid hormones level, rT3 including, suggests decrease in liver deiodinating activity in rats receiving lard.
*Supported by grant 5P06G02517 from the State Committee for Scientific Research
Piśmiennictwo
1. Mayes PA. Utlenianie kwasów tłuszczowych: Ketogeneza. In: Murray RK, Granner DK, Mayes PA, Rodwell VW, editors. Biochemia Harpera. Ed. III. Warszawa: Wydawnictwo Lekarskie PZWL; 1995. p. 260-73. 2.Cheema SK, Clandinin MT. Diet fat alters expression of genes for enzymes of lipogenesis in lean and obese mice. Biochem Biophys Acta 1996; 1, 299:284-88. 3.Raclot T, Oudart H. Selectivity of fatty acids on lipid metabolism and gene expression. Proc Nutr Soc 1999; 58:633-46. 4.Nakatani T, Kim HJ, Kaburagi Y et al. A low fish oil inhibits SREBP-1 proteolytic cascade, while a high-fish-oil feeding decreases SREBP-1 mRNA in mice liver: relationship to anti-obesity. J Lipid Res 2003; 44:369-79. 5.Tsuboyama-Kasaoka N, Takahashi M, Kim H. Up-regulation of liver uncoupling protein-2 mRNA by either fish oil feeding or fibrate administration in mice. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 1999; 257:879-85. 6.Blennemann B, Monn YK, Freake HC. Tissue-specific regulation of fatty acid synthesis by thyroid hormone. Endocrinology 1992; 130:637-43. 7. Feng X, Jiang Y, Meltzer P, Yen PM. Thyroid hormone regulation of hepatic genes in vivo detected by complementary DNA Microarray. Mol Endocrinol 2000; 14:947-55. 8.Viguerie N, Millet L, Avizou S, Vidal H, Larrouy D, Langin D. Regulation of human adipocyte gene expression by thyroid hormone. J Endocrinol Metab 2002; 87:630-4. 9.Hollander C. Free fatty acids: a possible regulator of free thyroid hormone levels in man. Endocrinol Metab 1967; 27:1219-23. 10. Tabachnick M, Korcek L. Effect of long-chain fatty acids on the binding of thyroxineand triiodothyronine to human thyroxine-binding globulin. Biochim Biophys Acta 1986; 881:292-6. 11.Suzuki Y, Nanno M, Gemma R, Yoshimi T. Plasma free fatty acids, inhibitor of extrathyroidal conversion of T4 to T3 and thyroid hormone binding inhibitor in patients with various nonthyroidal illnesses. Endocrinol Japan 1992; 39:445-53. 12.Lim CF, Munro S, Wynne K, Topliss D, Stockigt J. Influence of nonesterified fatty acids and lysolecithins on thyroxine binding to thyroxine-binding globulin and transthyretin. Thyroid 1995; 5:319-24. 13.Vermaak WJ, Kalk WJ, Kuyl JM, Smit AM. Fatty acid induced changes in circulating total and free thyroid hormones: in vitro effects and methodological artefacts. J Endocrinol Invest 1986; 9:121-6. 14.Otten MH., Hennemann G, Docter R, Visser TJ. The role of dietary fat in peripheral thyroid hormone metabolism. Metabolism 1980; 29:930-5. 15.Smith SM, Johnson P, Lukaski HC. In vitro hepatic thyroid hormone deiodination in iron-deficient rats: effect ofdietary fat. Life Sci 199; 353:603-9. 16.Takeuchi H, Matsuo T, Tokuyama K, Suzuki M. Serum triiodothyronine concentration and Na+, K+-ATPase activity in liver and skeletal muscle are influenced by dietary fat type in rats. J Nutr 1995; 125:2364-9. 17. Kahl S, Rosebrough RW, Elsasser TH. Hepatic iodothyronine 5´-monodeiodinase activity in the broiler chicken: effect of dietary fat and triiodothyronine (T3) supplementation. Nutr Res 1998; 18:1039-47. 18.Eder K, Skufca P, Brandsch C. Thermally oxidized dietary fats increase plasma thyroxine concentrations in rats irrespective of the vitamin E and selenium supply. J Nutr 2002; 132: 1275-81. 19. Svetina A, Jerkovic I, Vrabac L, Curicc S. Thyroid function, metabolic indices and growth performance in pigs fed 00-rapeseed meal. Acta Vet Hung 2003; 51: 283-95. 20.Noel-Suberville C, Pallet V, Audouin-Chevallier I et al. Expression of retinoic acid, triiodothyronine and glucocorticoid hormone nuclear receptors in decreased in the liver of rats fed a hypercholesteroilemia-inducing diet. Metabolism 1998; 47:301-8. 21.Bianco AC, Salvatore D, Gereben B, Berry MJ, Larsen PR. Biochemistry, cellular and molecular biology and physiological roles of the iodothyronine selenodeiodinases. Endocrine Rev 2002; 23:38-89.
