Patrycja Szalast1, Jacek Smereka2, Kurt Ruetzler3, Elzbieta Makomaska-Szaroszyk1, Kacper Kranc1, Kacper Stolarek1, Michal Paprocki1, *Lukasz Szarpak 1
Comparison of Airtraq® and Macintosh laryngoscope applied by nurses in manikins with normal and difficult airways: pilot data
Porównanie intubacji z wykorzystaniem Airtraq® i laryngoskopu Macintosha w warunkach normalnych i trudnych dróg oddechowych wykonywanej przez pielęgniarki. Badanie pilotażowe
1Lazarski University, Warsaw, Poland
2Department of Emergency Medical Service, Wroclaw Medical University, Poland
3Departments of Outcomes Research and General Anesthesiology, Cleveland Clinic, Cleveland, OH, USA
Streszczenie
Wstęp. Zabezpieczenie dróg oddechowych z wykorzystaniem rurki intubacyjnej stanowi obecnie złoty standard postępowania. Intubacja z wykorzystaniem laryngoskopii bezpośredniej w warunkach przedszpitalnych jest obarczona niewystarczającą skutecznością.
Cel pracy. Celem pracy było porównanie laryngoskopii bezpośredniej i wideolaryngoskopii podczas intubacji dotchawiczej w warunkach normalnych i trudnych dróg oddechowych wykonywanej przez pielęgniarki.
Materiał i metody. W badaniu udział wzięło 27 pielęgniarek. Protokół badania został zaakceptowany przez Radę Programową Polskiego Towarzystwa Medycyny Katastrof (zgoda: 32.04.2018.IRB). Badanie przeprowadzono w oparciu o randomizowany krzyżowy model badania. Jego uczestnicy wykonywali intubację z wykorzystaniem laryngoskopu z łopatką Macintosha (MAC) oraz wideolaryngoskopu Airtraq® (ATQ) w dwóch scenariuszach badawczych: scenariusz A – normalne drogi oddechowe, scenariusz B – trudne drogi oddechowe. W tym celu „pacjent” miał unieruchomiony odcinek szyjny kręgosłupa za pomocą standardowego jednoczęściowego kołnierza szyjnego.
Wyniki. Skuteczność pierwszej próby intubacji z wykorzystaniem MAC i ATQ była zróżnicowana zarówno w przypadku scenariusza A: odpowiednio 66,7 i 92,6% (p = 0,007), jak i podczas scenariusza B: 14,8 i 70,4% (p = 0,001). Mediana czasu intubacji podczas scenariusza A wynosiła odpowiednio 23 sek. (IQR: 22-33,5) dla MAC oraz 17 sek. (IQR: 15,5-25) dla ATQ (p = 0,031). W przypadku scenariusza B mediana czasu intubacji dla MAC i ATQ wynosiła odpowiednio: 53 sek. (IQR: 48-67) i 26 sek. (IQR: 24-49; p < 0,001).
Wnioski. W przeprowadzonym badaniu symulacyjnym pielęgniarki były w stanie z większą skutecznością wykonać intubację dotchawiczą z zastosowaniem wideolaryngoskopu Airtraq® aniżeli w oparciu o laryngoskopię bezpośrednią – zależność ta była obserwowana zarówno w warunkach normalnych, jak i trudnych dróg oddechowych.
Summary
Introduction. Endotracheal intubation is currently the gold standard of airway management. In direct laryngoscopy in pre-hospital settings, though, it turns out insufficiently effective.
Aim. The study purpose was to compare direct laryngoscopy and videolaryngoscopy for endotracheal intubation performed by nurses in normal and difficult airway conditions.
Material and methods. This randomized cross-over study involved 27 nurses. The protocol was approved by the Institutional Review Board of the Polish Society of Disaster Medicine (approval number: 32.04.2018.IRB). The participants performed intubation using a Macintosh laryngoscope (MAC) and an Airtraq® videolaryngoscope (ATQ) in 2 study scenarios: A – normal airway; B – difficult airway. For this latter purpose, the manikin had the cervical spine immobilized with a standard one-piece cervical collar.
Results. The effectiveness of the first intubation attempt with MAC and ATQ was varied both in scenario A: 66.7 and 92.6% (p = 0.007) and in scenario B: 14.8 and 70.4% (p = 0.001). The median intubation time in scenario A was 23 s (IQR: 22-33.5) for MAC and 17 s (IQR: 15.5-25) for ATQ (p = 0.031), respectively. In scenario B, this parameter value equaled 53 s (IQR: 48-67) for MAC and 26 s (IQR: 24-49) for ATQ (p < 0.001).
Conclusions. In the simulation study, nurses were able to perform endotracheal intubation with the use of ATQ with higher efficacy compared with direct laryngoscopy – this relationship was observed under both normal and difficult airway conditions.

INTRODUCTION
Tracheal intubation is currently one of the basic methods of airway management both in children and adults (1, 2). In some cases, such as cardiopulmonary resuscitation, endotracheal intubation is considered the gold standard of airway management. It allows for continuous chest compressions without the need for any interruptions for emergency breaths (3-5). However, it is recommended that endotracheal intubation should be performed by the most experienced person in the team (6, 7). This is due to the possibility of numerous potential complications, such as tooth injury, soft tissue damage and bleeding, epiglottis injury resulting from arytenoid cartilage dislocation or tracheal rupture and pneumomediastinum (8, 9).
Owing to its common availability, the most commonly applied endotracheal intubation technique is direct laryngoscopy with the use of Miller or Macintosh (MAC) blade laryngoscopes. However, the effectiveness of this method of intubation in pre-hospital conditions is insufficient (10, 11).
Alter et al. (12) indicate that the effectiveness of the first intubation attempt was 86% with the use of a MAC curved blade laryngoscope and 73% in the case of Miller laryngoscope. Sakles et al. (13), on the other hand, evaluated the effectiveness of intubation in an emergency department, indicating that the effectiveness of direct laryngoscopy was 86.6%. In the case of pediatric patients, the effectiveness of intubation is even lower than in adults (13-15). However, it is worth noting that in hospital conditions endotracheal intubation is usually performed by anesthesiologists or emergency physicians. In airway management applied in pre-hospital conditions, in an outpatient clinic, or by emergency medical service teams, paramedics and nurses can only rely on their own skills and knowledge. Therefore, the search for alternative endotracheal intubation methods is so important from the point of view of emergency medicine.
AIM
The aim of the study was to compare the effectiveness of endotracheal intubation based on direct laryngoscopy and videolaryngoscopy performed by nurses in normal and difficult airway conditions.
MATERIAL AND METHODS
Study design and participants
The study was designed as a prospective randomized cross-over simulation study. The protocol was approved by the Institutional Review Board of the Polish Society of Disaster Medicine (approval number: 32.04.2018.IRB). The research involved 27 nurses. Voluntary written informed consent was obtained from each participant. All participants were specialized in nursing in anesthesiology and intensive care or emergency medicine.
Simulation devices
Before the study, all participants took part in a training in endotracheal intubation with the use of direct laryngoscopy and videolaryngoscopy. At the end of the training, the correct technique of intubation with the use of MAC and ATQ was demonstrated. In the case of ATQ intubation, a special overlay was used for smartphone imaging (fig. 1).
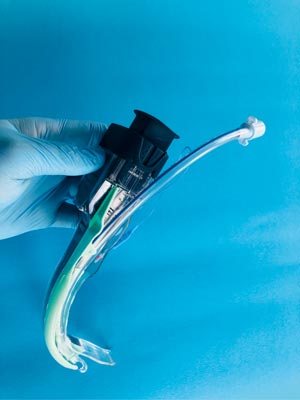
Fig. 1. Airtraq videolaryngoscope
Then the participants took part in a 30-minute practical training, during which they had the opportunity to practice intubation with the use of the tested techniques. For this purpose, an AT Kelly Torso (Laerdal, Stavanger, Norway) airway management manikin was used.
One week after the practical training, the nurses participated in the target study, during which they were asked to perform endotracheal intubation with the use of MAC and ATQ in 2 research scenarios: A – normal airway, B – difficult airway. For the latter purpose, the manikin had the cervical spine immobilized with a standard one-piece cervical collar.
An adult Resusci Anne simulator (Laerdal, Stavanger, Norway) was used to simulate a patient requiring immediate endotracheal intubation. The simulator was placed on a flat floor in a brightly lit room.
The participants were allowed one endotracheal intubation attempt. The order of both the participants and the research methods was random, determined with the coin toss technique. The detailed procedure of randomization is presented in figure 2.
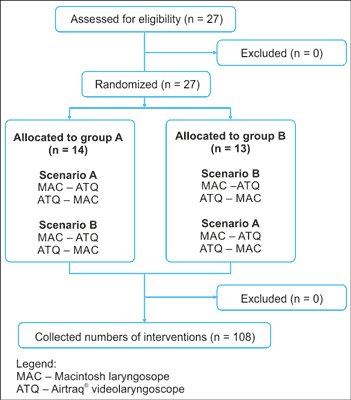
Fig. 2. Randomization flow chart
Measurements
The main parameter measured during the study was the effectiveness of the first endotracheal intubation attempt, defined by effective ventilation with a self-inflating bag connected to the endotracheal tube and the manikin chest rise during the ventilation attempt.
Additionally, the effectiveness of intubation was confirmed by specialized simulator software. Intubation time, defined as the time from grasping a laryngoscope to the chest rise with a ventilation attempt, was also measured, as well as the degree of glottis visibility in accordance with the Cormack-Lehane scale (16). After the intubation attempts, the participants evaluated the ease of intubation using a 100-degree visual analog scale (VAS), where 1 marked a procedure easy to perform and 100 – a procedure impossible to perform.
Statistical analysis
All statistical analyses were performed with the STATISTICA ver. 13.3 EN (StatSoft, Tulsa, OK, USA) software. All data are described as median values with an interquartile range (IQR) or numbers and percentages. Categorical variables were analyzed with the chi-square test. The Kruskal-Wallis test was applied to analyze differences in continuous variables between the 2 groups. Thereafter, post-hoc tests for the 2 groups were performed with the Mann-Whitney test. Statistical significance was assumed when the p-value was less than 0.05 in the two-sided test.
RESULTS
Study participants
Powyżej zamieściliśmy fragment artykułu, do którego możesz uzyskać pełny dostęp.
Mam kod dostępu
- Aby uzyskać płatny dostęp do pełnej treści powyższego artykułu albo wszystkich artykułów (w zależności od wybranej opcji), należy wprowadzić kod.
- Wprowadzając kod, akceptują Państwo treść Regulaminu oraz potwierdzają zapoznanie się z nim.
- Aby kupić kod proszę skorzystać z jednej z poniższych opcji.
Opcja #1
29 zł
Wybieram
- dostęp do tego artykułu
- dostęp na 7 dni
uzyskany kod musi być wprowadzony na stronie artykułu, do którego został wykupiony
Opcja #2
69 zł
Wybieram
- dostęp do tego i pozostałych ponad 7000 artykułów
- dostęp na 30 dni
- najpopularniejsza opcja
Opcja #3
129 zł
Wybieram
- dostęp do tego i pozostałych ponad 7000 artykułów
- dostęp na 90 dni
- oszczędzasz 78 zł
Piśmiennictwo
1. Bogdanski L, Truszewski Z, Kurowski A et al.: Simulated endotracheal intubation of a patient with cervical spine immobilization during resuscitation: a randomized comparison of the Pentax AWS, the Airtraq, and the McCoy Laryngoscopes. Am J Emerg Med 2015; 33(12): 1814-1817.
2. Szarpak L, Kurowski A, Czyzewski L et al.: Comparison of infant intubation through the TruView EVO2, TruView PCD, and Miller laryngoscope by paramedics during simulated infant cardiopulmonary resuscitation: A randomized crossover manikin study. Am J Emerg Med 2015; 33(7): 872-875.
3. Szarpak L, Madziala A, Czekajlo M et al.: Comparison of the UEScope videolaryngoscope with the Macintosh laryngoscope during simulated cardiopulmonary resuscitation: a randomized, cross-over, multi-center manikin study. Medicine (Baltimore) 2018; 97(36): e12085.
4. Szarpak L: Laryngoscopes for difficult airway scenarios: a comparison of the available devices. Expert Rev Med Devices 2018; 15(9): 631-643.
5. Driver BE, Prekker ME, Klein LR et al.: Effect of Use of a Bougie vs Endotracheal Tube and Stylet on First-Attempt Intubation Success Among Patients With Difficult Airways Undergoing Emergency Intubation: A Randomized Clinical Trial. JAMA 2018; 319(21): 2179-2189.
6. Smereka J, Czyzewski L, Szarpak L et al.: Comparison between the TrueView EVO2 PCD and direct laryngoscopy for endotracheal intubation performed by paramedics: Preliminary data. Am J Emerg Med 2017; 35(5): 789-790.
7. Ladny JR, Sierzantowicz R, Kedziora J et al.: Comparison of direct and optical laryngoscopy during simulated cardiopulmonary resuscitation. Am J Emerg Med 2017; 35(3): 518-519.
8. Szarpak L, Czyzewski L, Truszewski Z et al.: Comparison of Coopdech®, CoPilot®, Intubrite®, and Macintosh laryngoscopes for tracheal intubation during pediatric cardiopulmonary resuscitation: a randomized, controlled crossover simulation trial. Eur J Pediatr 2015; 174(11): 1517-1523.
9. Ahmed A, Azim A: Difficult tracheal intubation in critically ill. J Intensive Care 2018; 6: 49.
10. Ladny JR, Smereka J, Szarpak L: Comparison of the Trachway video intubating stylet and Macintosh laryngoscope for endotracheal intubation. Preliminary data. Am J Emerg Med 2017; 35(4): 574-575.
11. Karczewska K, Szarpak L, Smereka J et al.: ET-View compared to direct laryngoscopy in patients with immobilized cervical spine by unexperienced physicians: A randomized crossover manikin trial. Anaesthesiol Intensive Ther 2017; 49(4): 274-282.
12. Alter SM, Haim ED, Sullivan AH et al.: Intubation of prehospital patients with curved laryngoscope blade is more successful than with straight blade. Am J Emerg Med 2018; 36(10): 1807-1809.
13. Sakles JC, Mosier J, Chiu S et al.: A comparison of the C-MAC video laryngoscope to the Macintosh direct laryngoscope for intubation in the emergency department. Ann Emerg Med 2012; 60(6): 739-748.
14. Szarpak L, Czyzewski L, Kurowski A: Comparison of the Pentax, Truview, GlideScope, and the Miller laryngoscope for child intubation during resuscitation. Am J Emerg Med 2015; 33(3): 391-395.
15. Sakurai Y, Tamura M: Efficacy of the Airway Scope (Pentax-AWS) for training in pediatric intubation. Pediatr Int 2015; 57(2): 217-221.
16. Glosser L: Assessment of endotracheal tube intubation. Review of existing scales. Disaster Emerg Med J 2017; 2(2): 91-93.
17. Kleine-Brueggeney M, Greif R, Urwyler N et al.: The performance of rigid scopes for tracheal intubation: a randomised, controlled trial in patients with a simulated difficult airway. Anaesthesia 2016; 71(12): 1456-1463.
18. Ahmadi K, Ebrahimi M, Hashemian AM et al.: GlideScope Video Laryngoscope for Difficult Intubation in Emergency Patients: a Quasi-Randomized Controlled Trial. Acta Med Iran 2015; 53(12): 738-742.
19. Gómez-Ríos MÁ, Pinegger S, de Carrillo Mantilla M et al.: A randomised crossover trial comparing the Airtraq® NT, McGrath® MAC and Macintosh laryngoscopes for nasotracheal intubation of simulated easy and difficult airways in a manikin. Braz J Anesthesiol 2016; 66(3): 289-297.
20. Vargas M, Pastore A, Aloj F et al.: A comparison of videolaryngoscopes for tracheal intubation in predicted difficult airway: a feasibility study. BMC Anesthesiol 2017; 17(1): 25.
21. Truszewski Z, Czyzewski L, Marchese G et al.: Randomized crossover comparison of the AirTraq Avant® to the Macintosh laryngoscope for intubation with during simulated resuscitation by novice physicians. Am J Emerg Med 2016; 34(8): 1708-1709.
22. Pollard R, Wagner M, Grichnik K et al.: Prevalence of difficult intubation and failed intubation in a diverse obstetric community-based population. Curr Med Res Opin 2017; 33(12): 2167-2171.
23. Cook TM, Kelly FE: A national survey of videolaryngoscopy in the United Kingdom. Br J Anaesth 2017; 118(4): 593-600.
24. Kleine-Brueggeney M, Buttenberg M, Greif R et al.: Evaluation of three unchannelled videolaryngoscopes and the Macintosh laryngoscope in patients with a simulated difficult airway: a randomised, controlled trial. Anaesthesia 2017; 72(3): 370-378.
25. Ertürk T, Deniz S, Şimşek F et al.: Comparison of the Macintosh and Airtraq laryngoscopes in endotracheal intubation success. Turk J Anaesthesiol Reanim 2015; 43(3): 181-187.
26. Zhao H, Feng Y, Zhou Y: Teaching tracheal intubation: Airtraq is superior to Macintosh laryngoscope. BMC Med Educ 2014; 14: 144.
27. Castillo-Monzón CG, Marroquín-Valz HA, Fernández-Villacañas-Marín M et al.: Comparison of the Macintosh and Airtraq laryngoscopes in morbidly obese patients: a randomized and prospective study. J Clin Anesth 2017; 36: 136-141.
28. Das B, Samal RK, Ghosh A et al.: A randomised comparative study of the effect of Airtraq optical laryngoscope vs. Macintosh laryngoscope on intraocular pressure in non-ophthalmic surgery. Braz J Anesthesiol 2016; 66(1): 19-23.
29. Hoshijima H, Maruyama K, Mihara T et al.: Airtraq® reduces the hemodynamic response to tracheal intubation using single-lumen tubes in adults compared with the Macintosh laryngoscope: a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized control trials. J Clin Anesth 2018; 47: 86-94.
30. Wan L, Liao M, Li L et al.: McGrath Series 5 videolaryngoscope vs Airtraq DL videolaryngoscope for double-lumen tube intubation: a randomized trial. Medicine (Baltimore) 2016; 95(51): e5739.
31. Thakare DW, Malde AD: An observational study of feasibility of tracheal intubation using Airtraq in pediatric population. J Anaesthesiol Clin Pharmacol 2017; 33(3): 365-370.
32. Szarpak L, Karczewska K, Czyzewski L et al.: Airtraq laryngoscope versus the conventional Macintosh laryngoscope during pediatric intubation performed by nurses: a randomized crossover manikin study with three airway scenarios. Pediatr Emerg Care 2017; 33(11): 735-739.
33. Szarpak L, Karczewska K, Evrin T et al.: Comparison of intubation through the McGrath MAC, GlideScope, AirTraq, and Miller laryngoscope by paramedics during child CPR: a randomized crossover manikin trial. Am J Emerg Med 2015; 33(7): 946-950.
34. Owada G, Mihara T, Inagawa G et al.: A comparison of the Airtraq®, McGrath®, and Macintosh laryngoscopes for difficult paediatric intubation: a manikin study. PLoS One 2017; 12(2): e0171889.
35. Lee DW, Thampi S, Yap EP et al.: Evaluation of a smartphone camera system to enable visualization and image transmission to aid tracheal intubation with the Airtraq® laryngoscope. J Anesth 2016; 30(3): 514-517.
36. Hafner JW, Perkins BW, Korosac JD et al.: Intubation performance of advanced airway devices in a helicopter emergency medical service setting. Air Med J 2016; 35(3): 132-137.
37. Wang HE, Schmicker RH, Daya MR et al.: Effect of a strategy of initial laryngeal tube insertion vs endotracheal intubation on 72-hour survival in adults with out-of-hospital cardiac arrest: a randomized clinical trial. JAMA 2018; 320(8): 769-778.
38. Young Kim S, Park SO, Kim JW et al.: How much experience do rescuers require to achieve successful tracheal intubation during cardiopulmonary resuscitation? Resuscitation 2018; 133: 187-192.
39. Kurowski A, Hryniewicki T, Czyzewski L et al.: Simulation of blind tracheal intubation during pediatric cardiopulmonary resuscitation. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 2014; 190(11): 1315.
40. Truszewski Z, Szarpak L, Kurowski A et al.: Randomized trial of the chest compressions effectiveness comparing 3 feedback CPR devices and standard basic life support by nurses. Am J Emerg Med 2016; 34(3): 381-385.


